Health and medicine have always been central to human progress. From the earliest herbal remedies to modern-day surgeries and genomic therapies, medicine has continually evolved to improve life expectancy and quality of life. Today, we are living in an era of extraordinary medical advancements driven by science, technology, and global collaboration. Yet, alongside these innovations come new challenges, ranging from affordability and access to ethical concerns and health inequities.
This article explores the state of modern medicine, key innovations shaping the future of healthcare, challenges that persist, and strategies for building a healthier world.
The Changing Landscape of Healthcare
Over the past century, healthcare has undergone massive transformation. The discovery of antibiotics, the development of vaccines, organ transplants, and minimally invasive surgeries revolutionized how diseases are treated. Public health initiatives such as sanitation systems, safe water supplies, and nutrition programs have also played crucial roles in extending life expectancy.
In the 21st century, healthcare is becoming more patient-centered, technology-driven, and preventive-focused. The shift is no longer just about curing diseases but preventing them, predicting risks, and personalizing treatments.
Innovations Transforming Medicine
1. Precision Medicine
One of the most exciting advancements in healthcare is precision medicine—tailoring medical treatment to individual genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors. Instead of a one-size-fits-all approach, doctors can now analyze a patient’s genetic code to determine which treatments are most effective.
For example, cancer patients are increasingly receiving targeted therapies that focus on genetic mutations rather than general chemotherapy. This not only improves treatment outcomes but also reduces harmful side effects.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Healthcare
Artificial intelligence is playing a transformative role in diagnostics, research, and patient care. AI-powered tools can detect early signs of diseases like cancer or Alzheimer’s through medical imaging with remarkable accuracy. Algorithms can analyze vast datasets to identify health trends, predict outbreaks, and assist in drug discovery.
For patients, AI chatbots and virtual assistants offer round-the-clock health advice, improving accessibility in areas with limited healthcare professionals.
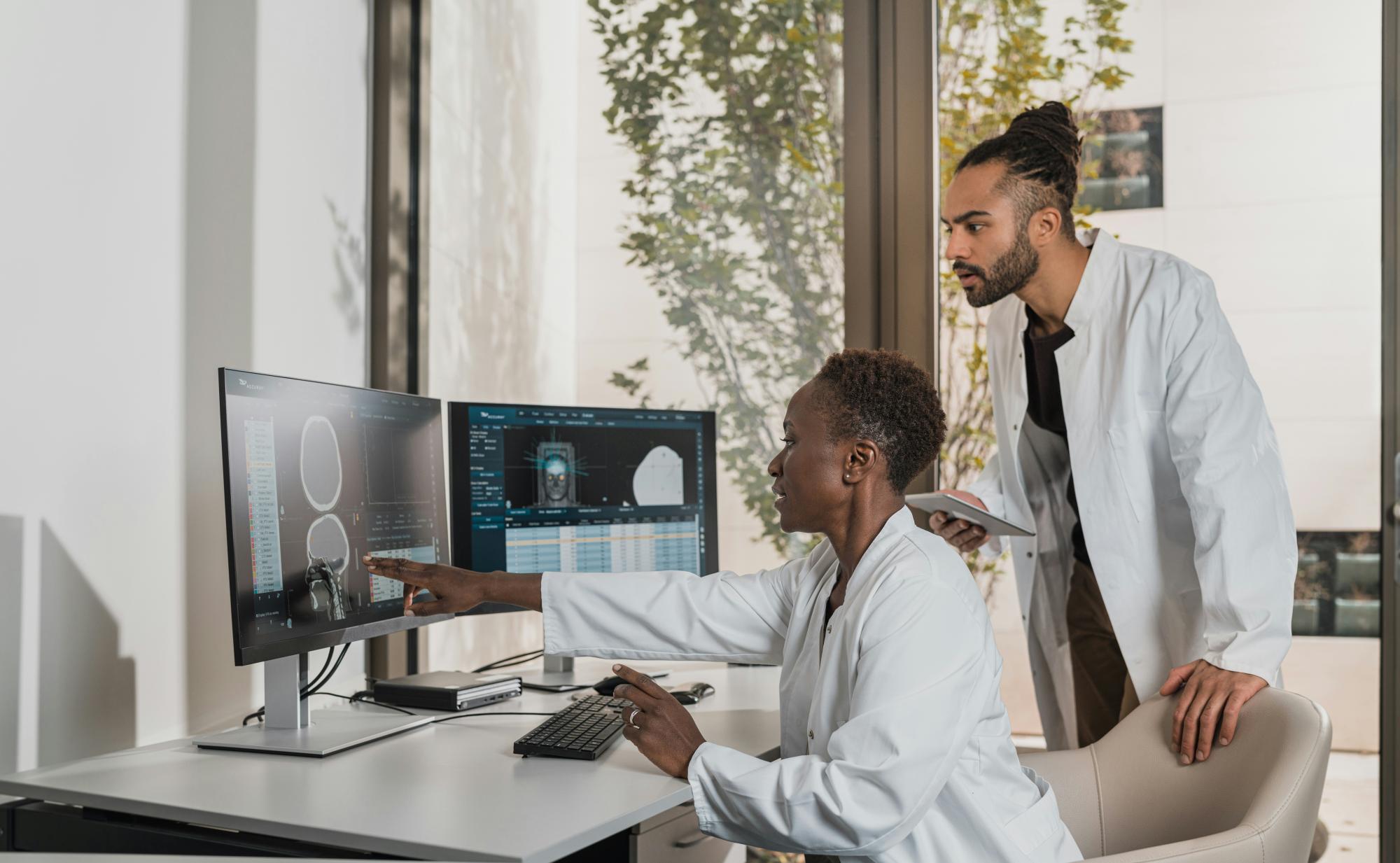

3. Telemedicine and Digital Health
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telemedicine—virtual doctor visits conducted via video calls. What began as a necessity is now becoming a permanent feature of healthcare systems worldwide. Telemedicine makes healthcare more accessible, particularly for people in remote or underserved areas.
Digital health apps and wearable devices also allow patients to monitor vital signs, track fitness, manage chronic conditions, and share data with healthcare providers in real time. This empowers individuals to take greater control over their health.
4. Biotechnology and Regenerative Medicine
Biotechnology is reshaping medicine through innovations like gene editing (CRISPR), stem cell therapy, and regenerative medicine. These technologies have the potential to cure genetic disorders, regenerate damaged tissues, and even grow replacement organs in laboratories.
For instance, clinical trials are underway using stem cells to repair spinal cord injuries and restore vision in patients with degenerative eye diseases. If widely adopted, such treatments could redefine healthcare in the coming decades.
5. Personalized Nutrition and Preventive Medicine
The saying “prevention is better than cure” is more relevant than ever. Advances in nutrition science, microbiome research, and wearable technology are leading to personalized diet plans that optimize health and prevent disease.
Preventive medicine—screenings, lifestyle interventions, and early detection—reduces long-term healthcare costs while improving quality of life. This shift toward prevention is essential for combating chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and obesity.
Persistent Challenges in Health and Medicine
Despite remarkable progress, significant challenges remain in making healthcare universally effective and accessible.
1. Global Health Inequalities
While advanced medical technologies are available in wealthy countries, billions of people in low- and middle-income regions lack access to basic healthcare. Issues such as poor infrastructure, shortages of healthcare workers, and high treatment costs exacerbate these inequalities.
2. Rising Healthcare Costs
Healthcare costs are skyrocketing globally, driven by expensive treatments, advanced technologies, and aging populations. For many families, medical expenses remain a leading cause of financial hardship. Achieving affordable healthcare remains a critical goal for policymakers.
3. Emerging Diseases and Pandemics
The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted vulnerabilities in global health systems. Emerging infectious diseases, antibiotic resistance, and climate-related health issues continue to pose major threats. Preparedness, global cooperation, and investment in research are crucial to prevent future crises.
4. Ethical and Privacy Concerns
Technological advancements raise ethical dilemmas. Who should have access to genetic data? How do we ensure patient privacy in a digital world? Should AI make life-or-death decisions? These questions must be addressed carefully to build trust and fairness in medicine.
5. Mental Health Crisis
Mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, and stress-related illnesses are rising globally. Unfortunately, mental health often receives less funding and attention than physical health. Integrating mental wellness into healthcare systems is essential for a holistic approach to health.
Opportunities for a Healthier Future
To overcome challenges and maximize opportunities, healthcare must focus on several key areas:
-
Universal Health Coverage (UHC): Ensuring access to affordable healthcare services for all people, regardless of income or location.
-
Public Health Investment: Expanding preventive measures such as vaccination, nutrition programs, and health education.
-
Sustainable Healthcare Systems: Reducing waste, embracing renewable energy in hospitals, and minimizing the carbon footprint of the medical industry.
-
Collaborative Innovation: Encouraging partnerships between governments, private companies, and research institutions to accelerate medical breakthroughs.
-
Health Equity: Addressing disparities in healthcare access, particularly for marginalized communities.
The Role of Patients in Modern Healthcare
In today’s world, patients are not passive recipients of care—they are active participants. With access to online health information, wearable devices, and telemedicine, individuals can make informed decisions and track their own health progress.
This empowerment, however, also comes with the responsibility of navigating accurate information and avoiding misinformation. Healthcare providers must guide patients in interpreting data responsibly while fostering trust and communication.
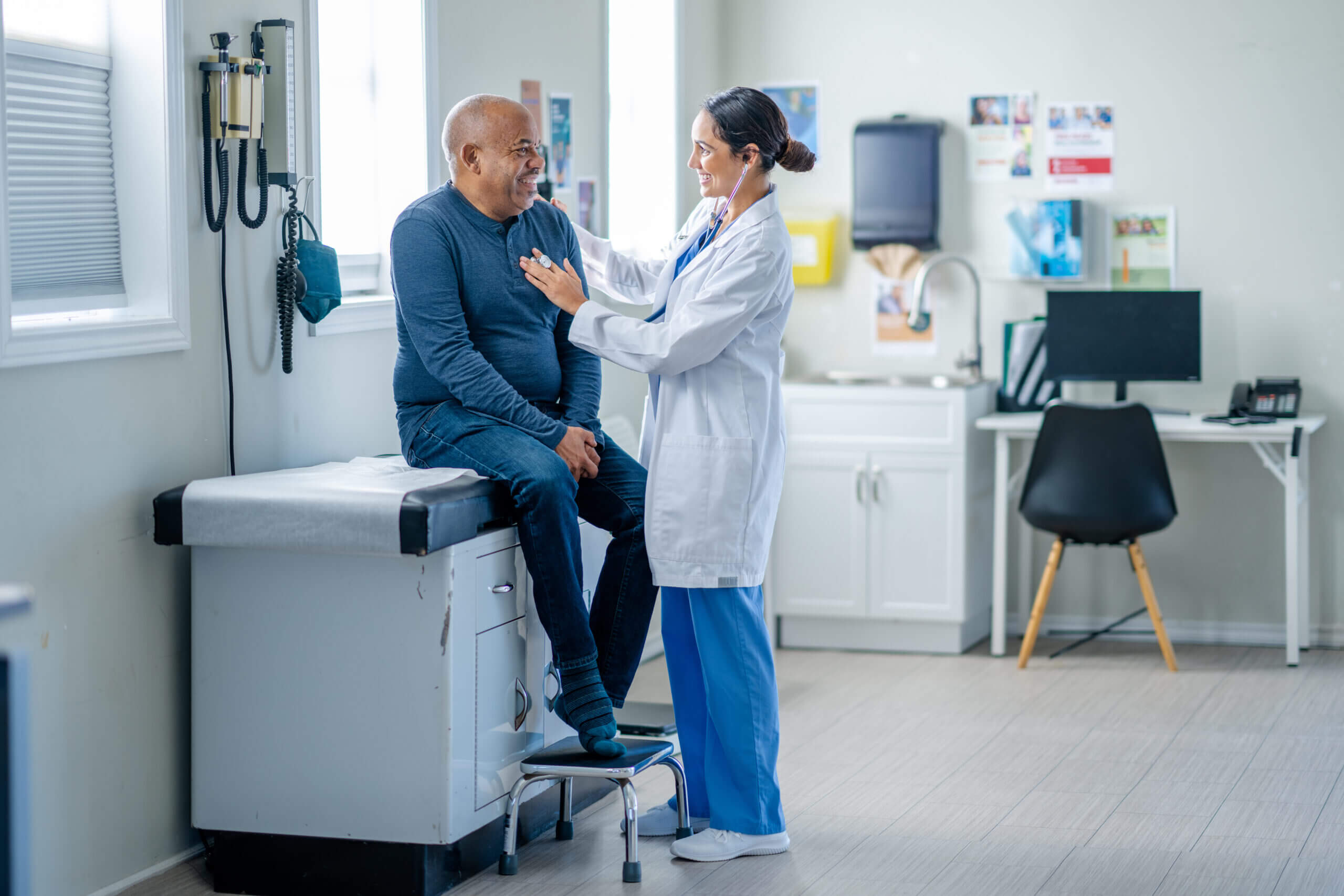

Conclusion: A Vision for the Future of Medicine
The field of health and medicine is on the cusp of unprecedented change. From AI-driven diagnostics to gene editing and telemedicine, innovation is improving outcomes, extending life expectancy, and making healthcare more patient-centered. At the same time, persistent challenges such as cost, inequality, and ethical dilemmas remind us that progress must be inclusive and responsible.
The future of medicine will not only be defined by technology but also by compassion, equity, and collaboration. By balancing innovation with accessibility and ethics, we can create a healthcare system that serves humanity as a whole—ensuring not just longer lives, but healthier and more fulfilling ones.

Leave a Reply